Understanding and Managing Baxter's Nerve: A Comprehensive Guide
Heel pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide. Among the various causes of heel pain, Baxter's nerve compression stands out as a significant contributor. In this detailed guide, we will explore the anatomy of Baxter's nerve, how it contributes to heel pain, and the best strategies for managing this condition effectively.
What is Baxter's Nerve?
Baxter's nerve is a small nerve located on the inside of your ankle, near your heel. It plays a crucial role in the sensation of the heel area. When this nerve becomes compressed, it can lead to 20% of chronic heel pain, causing discomfort and affecting daily activities.
Understanding the Anatomy
Baxter's nerve runs between the abductor hallucis muscle and the quadratus plantae muscle. These muscles are particularly developed in athletes and runners who frequently push off with their big toe. The nerve can be squeezed by these muscles, leading to pain and discomfort.
Symptoms of Baxter's Nerve Compression
Individuals with Baxter's nerve compression may experience symptoms such as numbness, burning, and tingling sensations in the heel. These symptoms often worsen throughout the day, especially with prolonged walking or standing.
Identifying the Signs
The hallmark of Baxter's nerve compression is a radiating heel pain that does not improve with typical treatments. If you notice persistent discomfort and soreness, it may be time to consider Baxter's nerve as a potential cause.
Effective Treatment Strategies
Managing Baxter's nerve compression involves a multi-faceted approach that includes both lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Let's explore the best ways to address this condition.
Reducing Inflammation
One of the primary goals in treating Baxter's nerve compression is to reduce inflammation. Here are some effective methods:
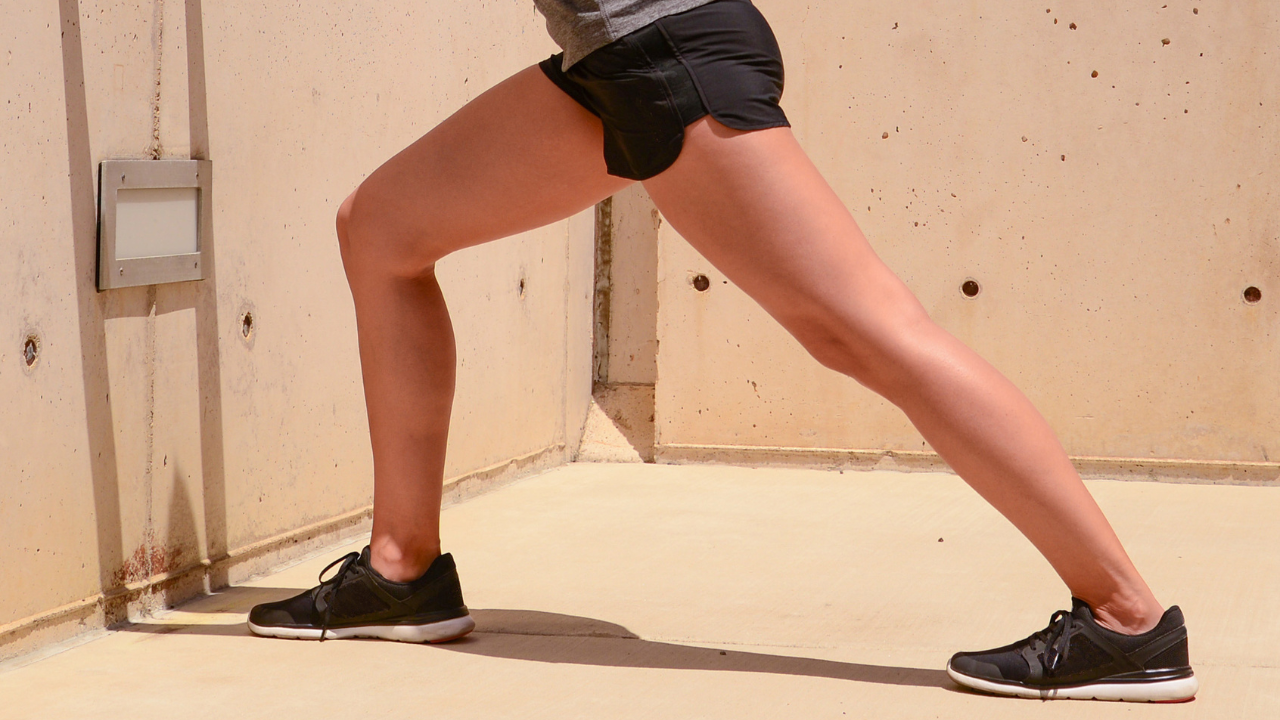
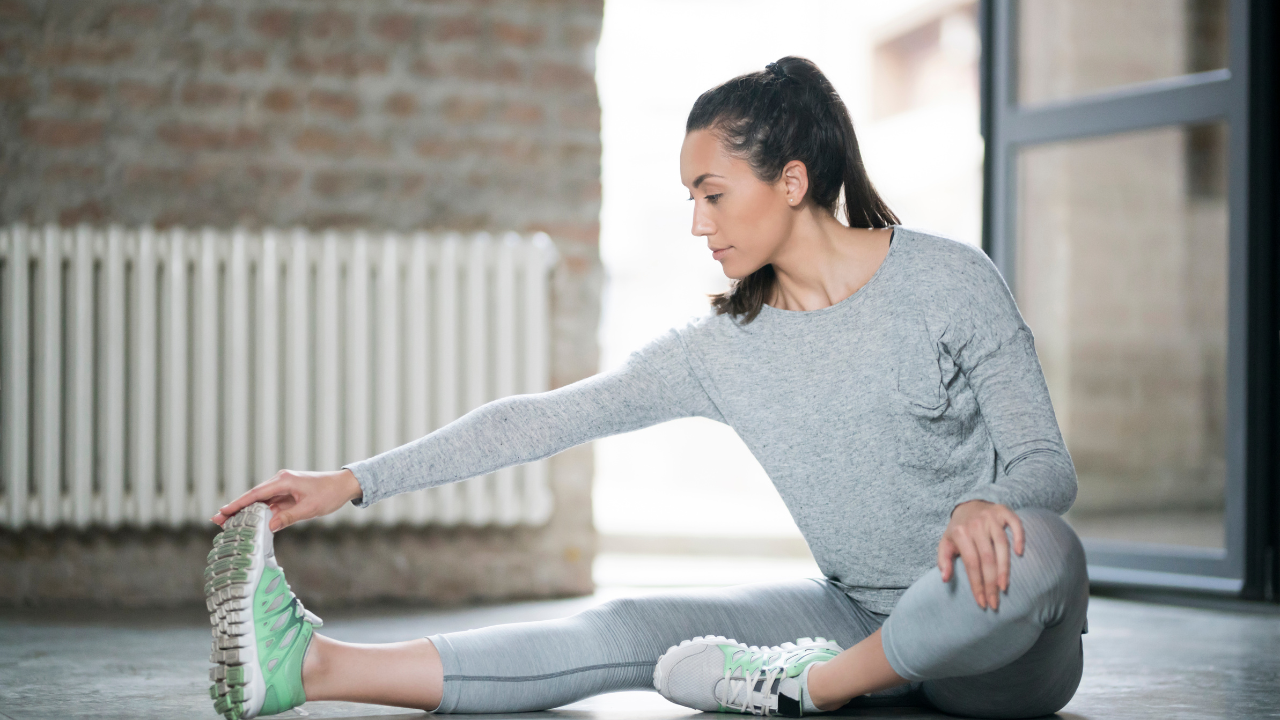
Stretching and Strengthening
Once inflammation is under control, focus on stretching and strengthening exercises to enhance flexibility and relieve nerve compression.
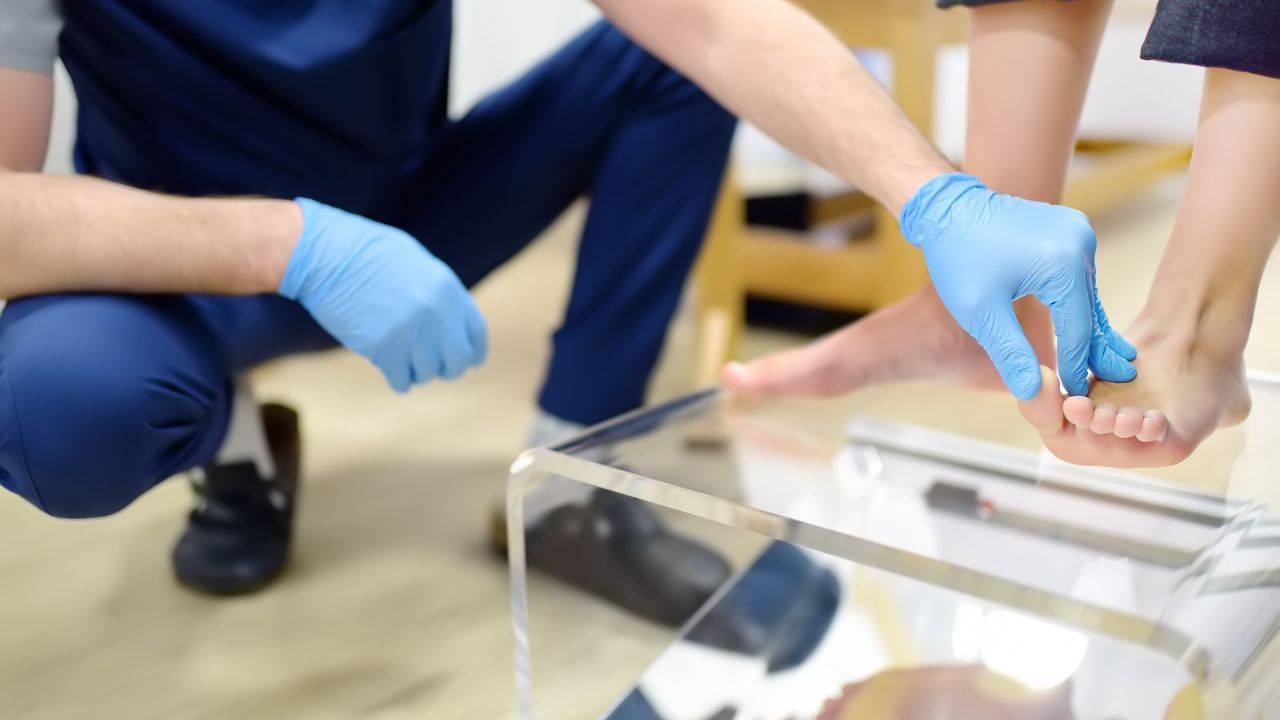
Consulting a Podiatrist
While self-care measures can be effective, consulting a podiatrist is crucial for diagnosing and treating underlying causes of heel pain. A podiatrist may recommend:
Advanced Treatment Options
In severe cases, more advanced treatments may be necessary:
Preventing Recurrence
Once the pain is managed, it's important to prevent recurrence by taking proactive steps:
Footwear and Orthotics
Choosing the right footwear and orthotics is key to preventing future issues:
Weight Management and Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy weight and modifying physical activities can significantly impact heel health:
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, coupled with strategic lifestyle modifications, play a pivotal role in promoting and preserving heel health.
As one of the most commonly overlooked aspects of foot care, the heels bear the brunt of our body weight, making it crucial to adopt practices that alleviate undue stress and potential injury.
Conclusion
Baxter's nerve compression is a manageable condition with the right approach. By understanding the anatomy, recognizing symptoms, and implementing effective treatment strategies, you can alleviate heel pain and improve your quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan and follow their recommendations for the best outcomes.
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide. We hope it helps you on your journey to pain-free living. For more information, check out our recommended products and resources in the show notes below. Don't forget to like and subscribe to our blog for more insightful content.





